Economia

- Ainda Mexe!...
"Phillips Curve for Advanced Economies on Period 1996-2007 - United States and Euro Area Case" Eduardo G. Manuel «We concluded that the true form of Phillips curve for short and long-run will not be verified always that exist equal evolution of their...
- O Que Tem Me Afastado Do Blog
Tenho postado pouco ultimamente. Por aqui o semestre vai chegando ao final... trazendo a tradicional alegria. Selecionei duas partes (de 4) de uma questão da prova de macro do ano passado. Enfim, tai pra quem quiser brincar. Não achei muito fácil,...
- Regra De Taylor
Explicado por Janet Yellen “For example, the Taylor rule is Rt = RR* + πt + 0.5(πt -2) + 0.5Yt, where R denotes the federal funds rate, RR* is the estimated value of the equilibrium real rate, π is the current inflation rate (usually...
- A Taxa Natural De Juros
Measuring the Natural Rate of Interest Thomas LaubachJohn C. WilliamsBoard of Governors of the Federal Reserve System ∗ November 2001 Abstract A key variable for the conduct of monetary policy is the natural rate of interest– the real interest...
- A Dinâmica Da Dívida Pública
There are two things that matter in government-debt dynamics: the difference between real interest rates and GDP growth (r-g), and the primary budget balance as a % of GDP (ie, before interest payments). In any given period the debt stock grows by the...
Economia
Keynes, Hayek, Wicksell - uma nova síntese


Rethinking the Keynesian Revolution: Keynes, Hayek, and the Wicksell Connection
Tyler Beck Goodspeed
Print publication date: 2012
Print ISBN-13: 9780199846658
Published to Oxford Scholarship Online: September 2012
DOI: 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199846658.001.0001
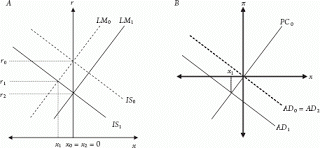
"... Though the derivation of the standard New Keynesian model is somewhat tedious and highly technical, it need not detain us here. Ultimately, the model can be distilled into threesimple equations. First, we have a forward-looking IS curve, reflecting optimal consumption by households. Since the standard model ignores investment, consumption demand is equivalent to aggregate demand and is a function of the interest rate and expected future consumption. The IS curve thus takes the form: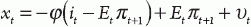 where xt is the output gap (the difference between current and potential or trend output, or what output would be in the absence of nominal rigidities), it the nominal interest rate, it – Etπt the real interest rate, πt the inflation rate, and νt a demand shock. The output gap is inversely related to the real interest rate owing to an intertemporal substitution effect—higher returns induce households to save more in the current period, which lowers current aggregate demand, and thus output. The output gap is also positively related to the expected future output gap, as households desire to smooth consumption over time; higher expected output in period t + 1 will therefore raise consumption demand in period t.
where xt is the output gap (the difference between current and potential or trend output, or what output would be in the absence of nominal rigidities), it the nominal interest rate, it – Etπt the real interest rate, πt the inflation rate, and νt a demand shock. The output gap is inversely related to the real interest rate owing to an intertemporal substitution effect—higher returns induce households to save more in the current period, which lowers current aggregate demand, and thus output. The output gap is also positively related to the expected future output gap, as households desire to smooth consumption over time; higher expected output in period t + 1 will therefore raise consumption demand in period t.
An aggregate supply curve assumes the form of a Phillips curve–like equation with Calvo-style monopolistic pricing (i.e., staggered price setting, which generates price “stickiness”), as follows: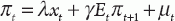
(p. 160 ) This New Keynesian Phillips curve, derived from the profit-maximizing price and output decisions of firms, thus gives inflation as a function of the output gap and expected future inflation, as well as random cost-push shocks (μt). Finally, a Taylor-style monetary policy rule constitutes the LM curve: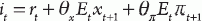
This is essentially a reaction function, relating the nominal interest rate chosen by the central bank to expected inflation and the expected output gap, so as to target a given real interest rate..."
Mais
Print ISBN-13: 9780199846658
Published to Oxford Scholarship Online: September 2012
DOI: 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199846658.001.0001
"... Though the derivation of the standard New Keynesian model is somewhat tedious and highly technical, it need not detain us here. Ultimately, the model can be distilled into threesimple equations. First, we have a forward-looking IS curve, reflecting optimal consumption by households. Since the standard model ignores investment, consumption demand is equivalent to aggregate demand and is a function of the interest rate and expected future consumption. The IS curve thus takes the form:
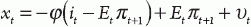 where xt is the output gap (the difference between current and potential or trend output, or what output would be in the absence of nominal rigidities), it the nominal interest rate, it – Etπt the real interest rate, πt the inflation rate, and νt a demand shock. The output gap is inversely related to the real interest rate owing to an intertemporal substitution effect—higher returns induce households to save more in the current period, which lowers current aggregate demand, and thus output. The output gap is also positively related to the expected future output gap, as households desire to smooth consumption over time; higher expected output in period t + 1 will therefore raise consumption demand in period t.
where xt is the output gap (the difference between current and potential or trend output, or what output would be in the absence of nominal rigidities), it the nominal interest rate, it – Etπt the real interest rate, πt the inflation rate, and νt a demand shock. The output gap is inversely related to the real interest rate owing to an intertemporal substitution effect—higher returns induce households to save more in the current period, which lowers current aggregate demand, and thus output. The output gap is also positively related to the expected future output gap, as households desire to smooth consumption over time; higher expected output in period t + 1 will therefore raise consumption demand in period t.An aggregate supply curve assumes the form of a Phillips curve–like equation with Calvo-style monopolistic pricing (i.e., staggered price setting, which generates price “stickiness”), as follows:
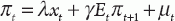
(p. 160 ) This New Keynesian Phillips curve, derived from the profit-maximizing price and output decisions of firms, thus gives inflation as a function of the output gap and expected future inflation, as well as random cost-push shocks (μt). Finally, a Taylor-style monetary policy rule constitutes the LM curve:
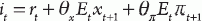
This is essentially a reaction function, relating the nominal interest rate chosen by the central bank to expected inflation and the expected output gap, so as to target a given real interest rate..."
Mais
loading...
- Ainda Mexe!...
"Phillips Curve for Advanced Economies on Period 1996-2007 - United States and Euro Area Case" Eduardo G. Manuel «We concluded that the true form of Phillips curve for short and long-run will not be verified always that exist equal evolution of their...
- O Que Tem Me Afastado Do Blog
Tenho postado pouco ultimamente. Por aqui o semestre vai chegando ao final... trazendo a tradicional alegria. Selecionei duas partes (de 4) de uma questão da prova de macro do ano passado. Enfim, tai pra quem quiser brincar. Não achei muito fácil,...
- Regra De Taylor
Explicado por Janet Yellen “For example, the Taylor rule is Rt = RR* + πt + 0.5(πt -2) + 0.5Yt, where R denotes the federal funds rate, RR* is the estimated value of the equilibrium real rate, π is the current inflation rate (usually...
- A Taxa Natural De Juros
Measuring the Natural Rate of Interest Thomas LaubachJohn C. WilliamsBoard of Governors of the Federal Reserve System ∗ November 2001 Abstract A key variable for the conduct of monetary policy is the natural rate of interest– the real interest...
- A Dinâmica Da Dívida Pública
There are two things that matter in government-debt dynamics: the difference between real interest rates and GDP growth (r-g), and the primary budget balance as a % of GDP (ie, before interest payments). In any given period the debt stock grows by the...
